管理运行#
本文档将指导您如何使用 CLI、SDK 和 VS Code 扩展管理您的运行。
一般情况
对于
CLI,您可以在终端中运行pf/pfazure run --help查看帮助消息。对于
SDK,您可以参考 Promptflow Python 库参考 并查看PFClient.runs以获取更多运行操作。
我们来看看以下主题
创建运行#
要针对批量输入创建运行,您可以编写以下 YAML 文件。
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/promptflow/latest/Run.schema.json
flow: ../web_classification
data: ../webClassification1.jsonl
column_mapping:
url: "${data.url}"
variant: ${summarize_text_content.variant_0}
要针对现有运行创建运行,您可以编写以下 YAML 文件。
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/promptflow/latest/Run.schema.json
flow: ../classification_accuracy_evaluation
data: ../webClassification1.jsonl
column_mapping:
groundtruth: "${data.answer}"
prediction: "${run.outputs.category}"
run: <existing-flow-run-name>
有关列映射的详细信息,请参考此处。您可以在 运行 YAML 架构 中找到有关流 YAML 架构的更多信息。
准备好 YAML 文件后,使用以下 CLI 命令创建它们
# create the flow run
pf run create -f <path-to-flow-run>
# create the flow run and stream output
pf run create -f <path-to-flow-run> --stream
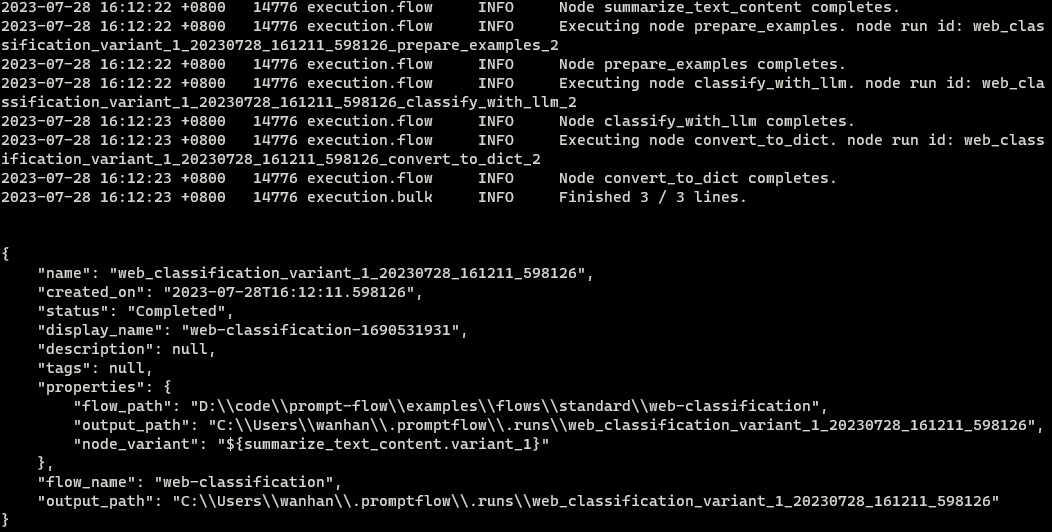
如果运行创建成功,预期结果如下。
使用 SDK,创建 Run 对象并使用 PFClient 提交。以下代码片段展示了如何导入所需类并创建运行
from promptflow.client import PFClient
from promptflow.entities import Run
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# Initialize an Run object
run = Run(
flow="<path-to-local-flow>",
# run flow against local data or existing run, only one of data & run can be specified.
data="<path-to-data>",
run="<existing-run-name>",
column_mapping={"url": "${data.url}"},
variant="${summarize_text_content.variant_0}"
)
# Create the run
result = pf.runs.create_or_update(run)
print(result)
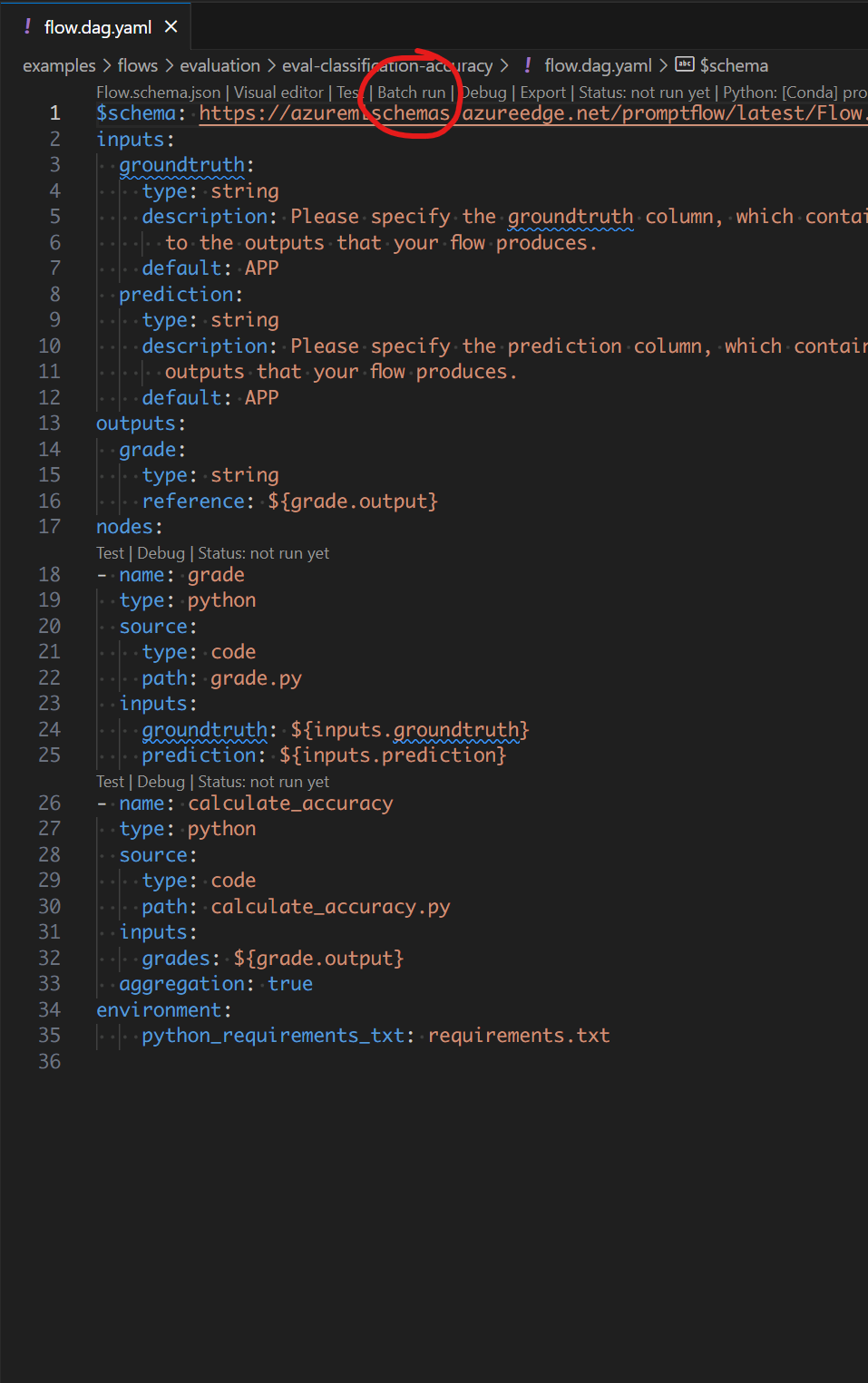
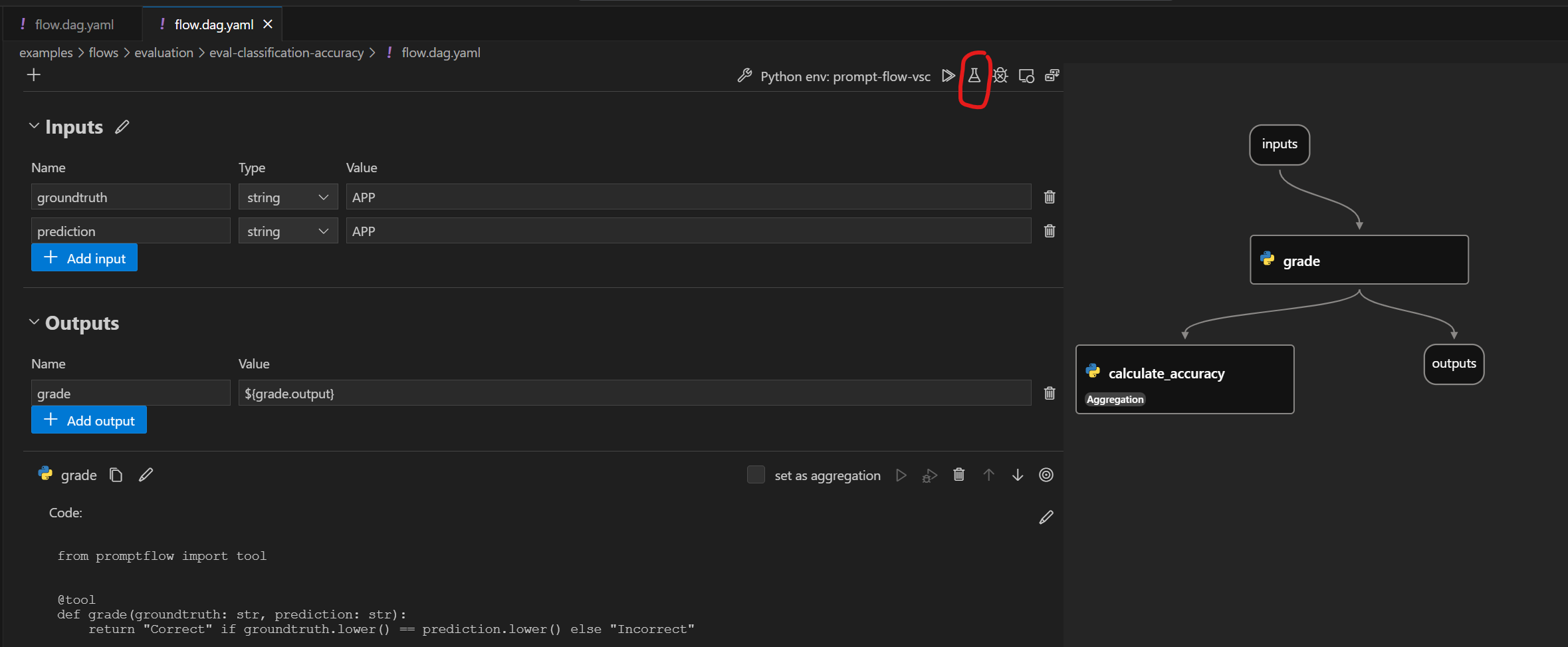
您可以点击默认 YAML 编辑器顶部或 flow.dag.yaml 文件的可视化编辑器中的操作,以触发流批量运行。
获取运行#
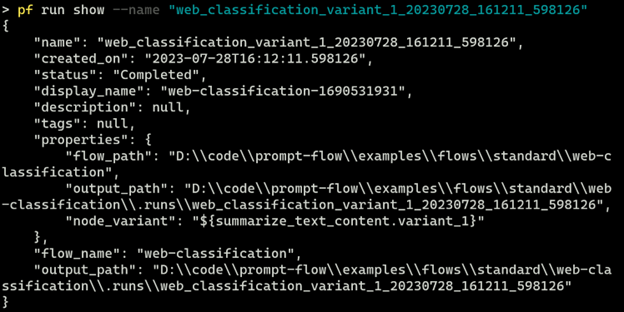
以 JSON 格式在 CLI 中获取运行。
pf run show --name <run-name>
使用 PFClient 显示运行
from promptflow.client import PFClient
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# Get and print the run
run = pf.runs.get(name="<run-name>")
print(run)
显示运行详情#
以 TABLE 格式获取运行详情。
pf run show-details --name <run-name>
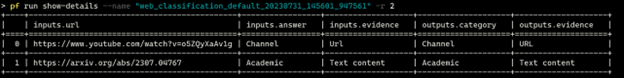
使用 PFClient 显示运行详情
from promptflow.client import PFClient
from tabulate import tabulate
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# Get and print the run-details
run_details = pf.runs.get_details(name="<run-name>")
print(tabulate(details.head(max_results), headers="keys", tablefmt="grid"))

显示运行指标#
以 JSON 格式获取运行指标。
pf run show-metrics --name <run-name>

使用 PFClient 显示运行指标
from promptflow.client import PFClient
import json
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# Get and print the run-metrics
run_details = pf.runs.get_metrics(name="<run-name>")
print(json.dumps(metrics, indent=4))
可视化运行#
在浏览器中可视化运行。
pf run visualize --names <run-name>
浏览器将打开并显示运行输出。
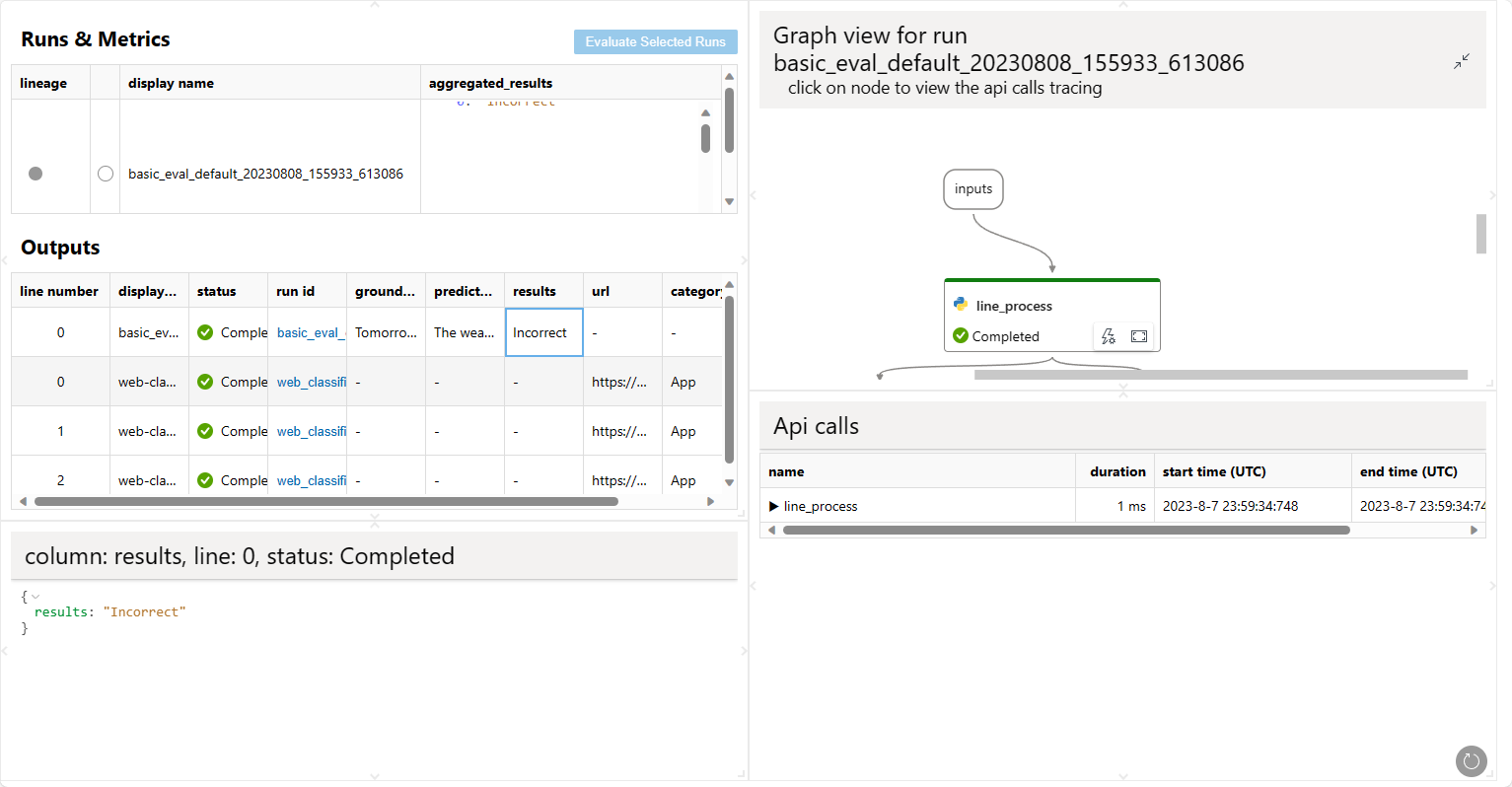
使用 PFClient 可视化运行
from promptflow.client import PFClient
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# Visualize the run
client.runs.visualize(runs="<run-name>")
在 VS Code 主侧边栏 > prompt flow 面板中,有一个运行列表。它将列出您机器上的所有运行。选择一个或多个项目,然后点击右上角的“可视化”按钮以可视化本地运行。
列出运行#
以 JSON 格式列出运行。
pf run list
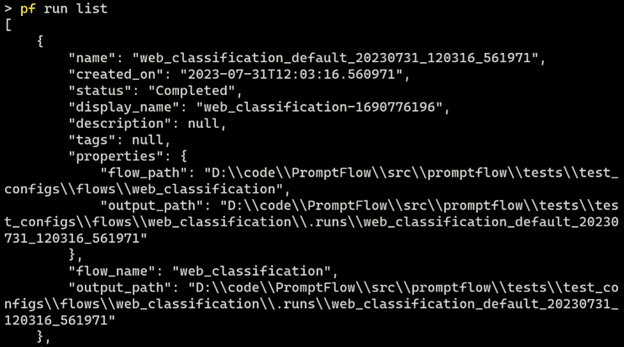
使用 PFClient 列出
from promptflow.client import PFClient
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# list runs
runs = pf.runs.list()
print(runs)
在 VS Code 主侧边栏 > prompt flow 面板中,有一个运行列表。它将列出您机器上的所有运行。将鼠标悬停在上面可以查看更多详细信息。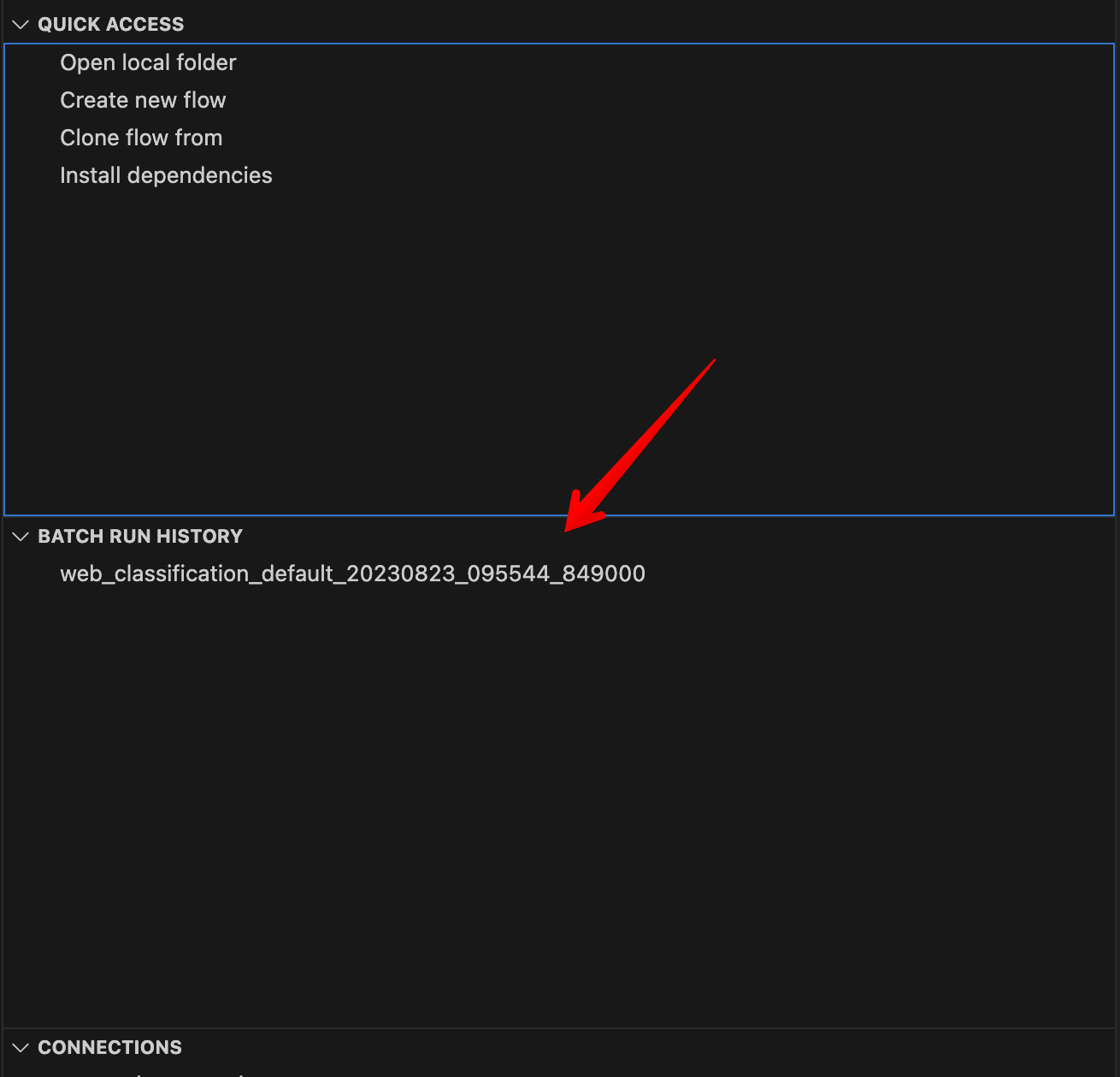
更新运行#
以 JSON 格式获取运行指标。
pf run update --name <run-name> --set display_name=new_display_name
使用 PFClient 更新运行
from promptflow.client import PFClient
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# Get and print the run-metrics
run = pf.runs.update(name="<run-name>", display_name="new_display_name")
print(run)
归档运行#
归档运行,使其不会显示在运行列表结果中。
pf run archive --name <run-name>
使用 PFClient 归档
from promptflow.client import PFClient
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# archive a run
client.runs.archive(name="<run-name>")

恢复运行#
恢复已归档的运行,使其可以显示在运行列表结果中。
pf run restore --name <run-name>
使用 PFClient 恢复
from promptflow.client import PFClient
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# restore a run
client.runs.restore(name="<run-name>")
删除运行#
注意:pf run delete 操作不可逆。此操作将永久从您的本地磁盘中删除运行。运行实体和输出数据都将被删除。
如果运行名称无效,删除将失败。
pf run delete --name <run-name>
使用 PFClient 删除
from promptflow.client import PFClient
# Get a pf client to manage runs
pf = PFClient()
# delete a run
client.runs.delete(name="run-name")