ai-agents-for-beginners
探索 Microsoft Agent 框架
引言
本课程将涵盖
- 了解 Microsoft Agent 框架:主要功能和价值
- 探索 Microsoft Agent 框架的关键概念
- MAF 与 Semantic Kernel 和 AutoGen 的比较:迁移指南
学习目标
完成本课程后,您将了解如何
- 使用 Microsoft Agent 框架构建可用于生产环境的 AI 代理
- 将 Microsoft Agent 框架的核心功能应用于您的代理用例
- 迁移和集成现有的代理框架和工具
代码示例
Microsoft Agent 框架 (MAF) 的代码示例可在本存储库的 xx-python-agent-framework 和 xx-dotnet-agent-framework 文件中找到。
了解 Microsoft Agent 框架
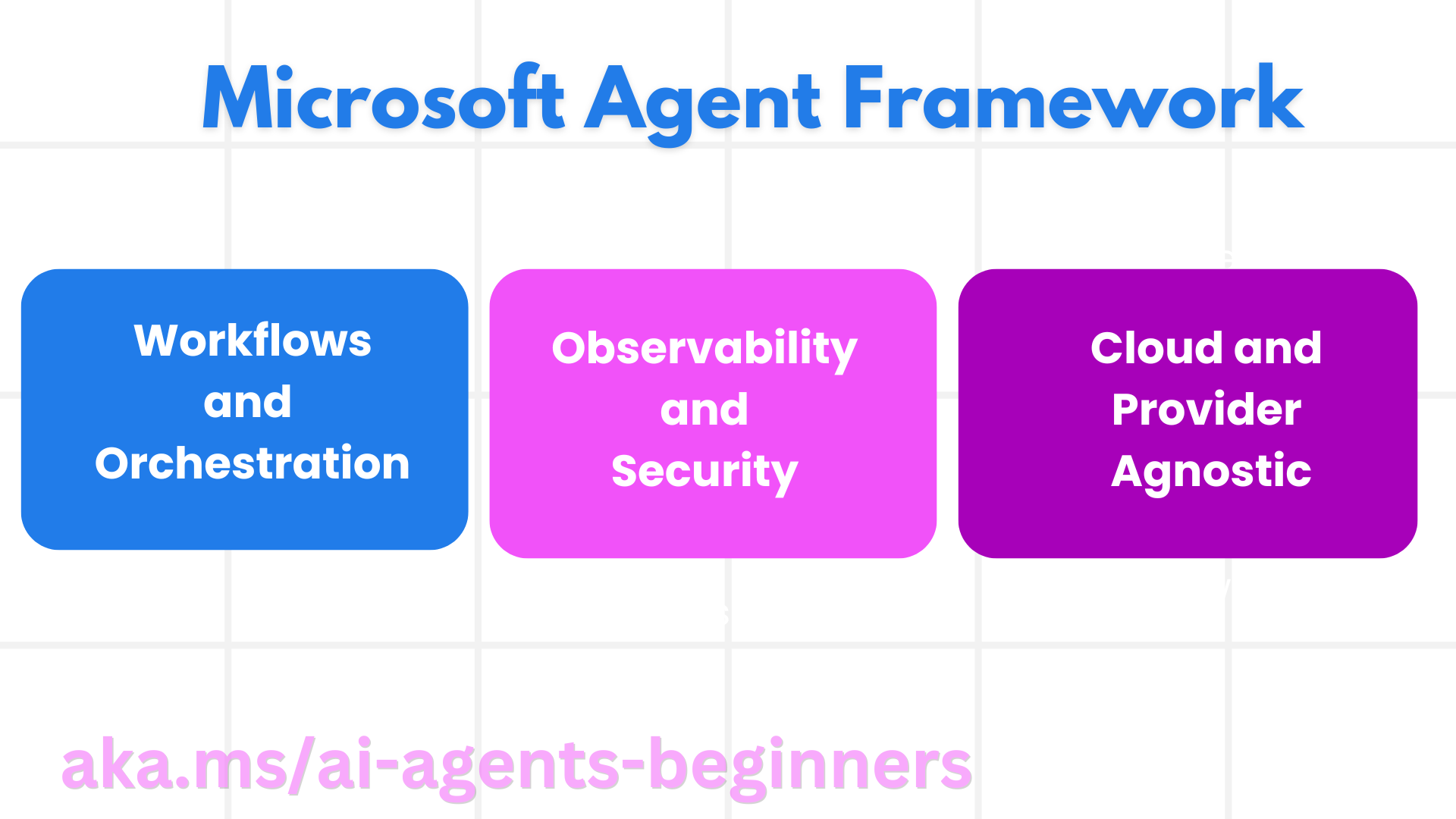
Microsoft Agent 框架 (MAF) 基于 Semantic Kernel 和 AutoGen 的经验和学习成果构建。它提供了灵活性,以应对生产和研究环境中出现的各种代理用例,包括
- 顺序代理编排,适用于需要分步工作流的场景。
- 并发编排,适用于代理需要同时完成任务的场景。
- 群聊编排,适用于代理可以协同完成一项任务的场景。
- 交接编排,适用于子任务完成后代理之间相互交接任务的场景。
- 磁性编排,适用于管理器代理创建和修改任务列表并处理子代理协调以完成任务的场景。
为了在生产环境中交付 AI 代理,MAF 还包括以下功能
- 可观测性,通过使用 OpenTelemetry,在 Azure AI Foundry 仪表板上实现对 AI 代理的每个操作(包括工具调用、编排步骤、推理流程和性能监控)的观测。
- 安全性,通过在 Azure AI Foundry 上原生托管代理,其中包括角色访问控制、私有数据处理和内置内容安全等安全控制。
- 持久性,因为代理线程和工作流可以暂停、恢复并从错误中恢复,从而支持更长时间的运行过程。
- 控制,支持人工介入工作流,其中任务被标记为需要人工批准。
Microsoft Agent 框架还致力于通过以下方式实现互操作性
- 与云无关 - 代理可以在容器、本地和多个不同的云中运行。
- 与提供商无关 - 代理可以通过您首选的 SDK 创建,包括 Azure OpenAI 和 OpenAI
- 集成开放标准 - 代理可以利用 Agent-to-Agent (A2A) 和模型上下文协议 (MCP) 等协议来发现和使用其他代理和工具。
- 插件和连接器 - 可以与 Microsoft Fabric、SharePoint、Pinecone 和 Qdrant 等数据和内存服务建立连接。
让我们看看这些功能如何应用于 Microsoft Agent 框架的一些核心概念。
Microsoft Agent 框架的关键概念
智能体
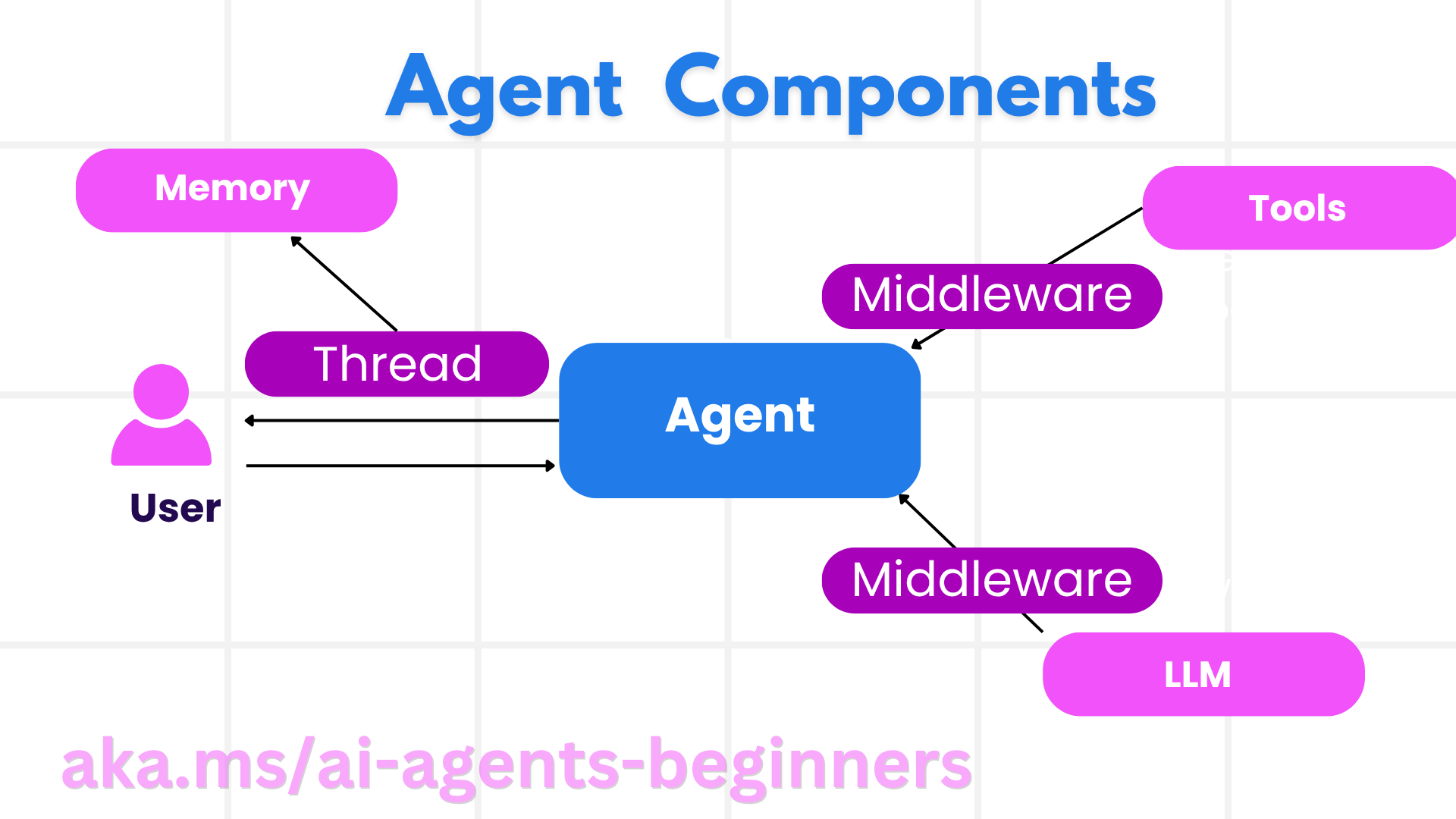
创建代理
通过定义推理服务(LLM 提供商)、AI 代理要遵循的一组指令以及分配的 name 来完成代理创建
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential()).create_agent( instructions="You are good at recommending trips to customers based on their preferences.", name="TripRecommender" )
上面使用的是 Azure OpenAI,但代理可以使用各种服务创建,包括 Azure AI Foundry Agent Service
AzureAIAgentClient(async_credential=credential).create_agent( name="HelperAgent", instructions="You are a helpful assistant." ) as agent
OpenAI Responses、ChatCompletion API
agent = OpenAIResponsesClient().create_agent( name="WeatherBot", instructions="You are a helpful weather assistant.", )
agent = OpenAIChatClient().create_agent( name="HelpfulAssistant", instructions="You are a helpful assistant.", )
或使用 A2A 协议的远程代理
agent = A2AAgent( name=agent_card.name, description=agent_card.description, agent_card=agent_card, url="https://your-a2a-agent-host" )
运行代理
代理使用 .run 或 .run_stream 方法运行,用于非流式或流式响应。
result = await agent.run("What are good places to visit in Amsterdam?")
print(result.text)
async for update in agent.run_stream("What are the good places to visit in Amsterdam?"):
if update.text:
print(update.text, end="", flush=True)
每次代理运行还可以选择自定义参数,例如代理使用的 max_tokens、代理可以调用的 tools,甚至是用于代理的 model 本身。
这在完成用户任务需要特定模型或工具的情况下非常有用。
工具
工具可以在定义代理时定义
def get_attractions( location: Annotated[str, Field(description="The location to get the top tourist attractions for")], ) -> str: """Get the top tourist attractions for a given location.""" return f"The top attractions for {location} are."
# When creating a ChatAgent directly
agent = ChatAgent( chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(), instructions="You are a helpful assistant", tools=[get_attractions]
也可以在运行代理时定义
result1 = await agent.run( "What's the best place to visit in Seattle?", tools=[get_attractions] # Tool provided for this run only )
代理线程
代理线程用于处理多轮对话。线程可以通过以下方式创建
- 使用
get_new_thread(),使线程能够长时间保存 - 在运行代理时自动创建线程,并且线程仅在当前运行期间持续。
创建线程的代码如下
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, I am here to help you book travel. Where would you like to go?", thread=thread)
然后可以将线程序列化以供以后使用
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread()
# Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, how are you?", thread=thread)
# Serialize the thread for storage.
serialized_thread = await thread.serialize()
# Deserialize the thread state after loading from storage.
resumed_thread = await agent.deserialize_thread(serialized_thread)
代理中间件
代理与工具和 LLM 交互以完成用户任务。在某些情况下,我们希望在这些交互之间执行或跟踪。代理中间件使我们能够通过以下方式实现这一点
函数中间件
此中间件允许我们在代理和它将调用的函数/工具之间执行一个动作。一个示例是您可能希望对函数调用进行一些日志记录。
在下面的代码中,next 定义是应该调用下一个中间件还是实际函数。
async def logging_function_middleware(
context: FunctionInvocationContext,
next: Callable[[FunctionInvocationContext], Awaitable[None]],
) -> None:
"""Function middleware that logs function execution."""
# Pre-processing: Log before function execution
print(f"[Function] Calling {context.function.name}")
# Continue to next middleware or function execution
await next(context)
# Post-processing: Log after function execution
print(f"[Function] {context.function.name} completed")
聊天中间件
此中间件允许我们在代理和 LLM 之间的请求之间执行或记录一个动作。
这包含重要信息,例如发送到 AI 服务的 messages。
async def logging_chat_middleware(
context: ChatContext,
next: Callable[[ChatContext], Awaitable[None]],
) -> None:
"""Chat middleware that logs AI interactions."""
# Pre-processing: Log before AI call
print(f"[Chat] Sending {len(context.messages)} messages to AI")
# Continue to next middleware or AI service
await next(context)
# Post-processing: Log after AI response
print("[Chat] AI response received")
代理记忆
如 代理记忆 课程中所述,记忆是使代理能够在不同上下文中操作的重要元素。MAF 提供了几种不同类型的记忆
内存存储
这是在应用程序运行时存储在线程中的记忆。
# Create a new thread.
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
response = await agent.run("Hello, I am here to help you book travel. Where would you like to go?", thread=thread)
持久消息
此记忆用于在不同会话中存储对话历史记录。它使用 chat_message_store_factory 定义
from agent_framework import ChatMessageStore
# Create a custom message store
def create_message_store():
return ChatMessageStore()
agent = ChatAgent(
chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(),
instructions="You are a Travel assistant.",
chat_message_store_factory=create_message_store
)
动态记忆
此记忆在代理运行之前添加到上下文中。这些记忆可以存储在外部服务中,例如 mem0
from agent_framework.mem0 import Mem0Provider
# Using Mem0 for advanced memory capabilities
memory_provider = Mem0Provider(
api_key="your-mem0-api-key",
user_id="user_123",
application_id="my_app"
)
agent = ChatAgent(
chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(),
instructions="You are a helpful assistant with memory.",
context_providers=memory_provider
)
代理可观测性
可观测性对于构建可靠和可维护的代理系统非常重要。MAF 与 OpenTelemetry 集成,提供跟踪和度量,以实现更好的可观测性。
from agent_framework.observability import get_tracer, get_meter
tracer = get_tracer()
meter = get_meter()
with tracer.start_as_current_span("my_custom_span"):
# do something
pass
counter = meter.create_counter("my_custom_counter")
counter.add(1, {"key": "value"})
工作流
MAF 提供预定义步骤的工作流来完成任务,并在这些步骤中包含 AI 代理作为组件。
工作流由不同的组件组成,这些组件允许更好的控制流。工作流还支持多代理编排和检查点以保存工作流状态。
工作流的核心组件是
执行器
执行器接收输入消息,执行其分配的任务,然后生成输出消息。这使工作流向前推进,以完成更大的任务。执行器可以是 AI 代理或自定义逻辑。
边
边用于定义工作流中消息的流向。这些可以是
直接边 - 执行器之间简单的一对一连接
from agent_framework import WorkflowBuilder
builder = WorkflowBuilder()
builder.add_edge(source_executor, target_executor)
builder.set_start_executor(source_executor)
workflow = builder.build()
条件边 - 在满足特定条件后激活。例如,当酒店房间不可用时,执行器可以建议其他选项。
开关案例边 - 根据定义的条件将消息路由到不同的执行器。例如,如果旅行客户拥有优先访问权限,他们的任务将通过另一个工作流处理。
扇出边 - 将一条消息发送到多个目标。
扇入边 - 从不同的执行器收集多条消息并发送到一个目标。
事件
为了提供更好的工作流可观测性,MAF 提供了内置的执行事件,包括
WorkflowStartedEvent- 工作流执行开始WorkflowOutputEvent- 工作流产生输出WorkflowErrorEvent- 工作流遇到错误ExecutorInvokeEvent- 执行器开始处理ExecutorCompleteEvent- 执行器完成处理RequestInfoEvent- 发出请求
从其他框架(Semantic Kernel 和 AutoGen)迁移
MAF 与 Semantic Kernel 的区别
简化代理创建
Semantic Kernel 依赖于为每个代理创建内核实例。MAF 采用简化的方法,通过为主要提供商使用扩展。
agent = AzureOpenAIChatClient(credential=AzureCliCredential()).create_agent( instructions="You are good at reccomending trips to customers based on their preferences.", name="TripRecommender" )
代理线程创建
Semantic Kernel 需要手动创建线程。在 MAF 中,代理直接分配一个线程。
thread = agent.get_new_thread() # Run the agent with the thread.
工具注册
在 Semantic Kernel 中,工具注册到内核,然后内核传递给代理。在 MAF 中,工具在代理创建过程中直接注册。
agent = ChatAgent( chat_client=OpenAIChatClient(), instructions="You are a helpful assistant", tools=[get_attractions]
MAF 与 AutoGen 的区别
团队与工作流
Teams 是 AutoGen 中代理事件驱动活动的事件结构。MAF 使用 Workflows,通过基于图的架构将数据路由到执行器。
工具创建
AutoGen 使用 FunctionTool 包装函数供代理调用。MAF 使用 @ai_function,其操作类似,但也会自动推断每个函数的模式。
代理行为
AutoGen 中的代理默认是单轮代理,除非 max_tool_iterations 设置得更高。在 MAF 中,ChatAgent 默认是多轮的,这意味着它会继续调用工具直到用户任务完成。
代码示例
Microsoft Agent 框架的代码示例可在本存储库的 xx-python-agent-framework 和 xx-dotnet-agent-framework 文件中找到。
对 Microsoft Agent 框架有更多疑问?
加入 Azure AI Foundry Discord,与其他学习者交流,参加办公时间,并解答您的 AI 代理问题。