ai-agents-for-beginners
(点击上方图片观看本课程视频)
工具使用设计模式
工具很有趣,因为它们允许 AI Agent 拥有更广泛的功能。通过添加工具,Agent 可以执行多种操作,而不是仅限于执行有限的动作。在本章中,我们将探讨工具使用设计模式,它描述了 AI Agent 如何使用特定工具来达到其目标。
引言
在本课程中,我们将回答以下问题:
- 什么是工具使用设计模式?
- 它适用于哪些用例?
- 实现该设计模式所需的元素/构建模块是什么?
- 使用工具使用设计模式构建可信赖的 AI Agent 有哪些特殊考量?
学习目标
完成本课程后,您将能够:
- 定义工具使用设计模式及其目的。
- 识别工具使用设计模式适用的用例。
- 理解实现设计模式所需的关键元素。
- 识别在使用此设计模式的 AI Agent 中确保可信度的考量。
什么是工具使用设计模式?
工具使用设计模式专注于赋予大型语言模型(LLM)与外部工具交互以实现特定目标的能力。工具是可由 Agent 执行以执行操作的代码。工具可以是简单的函数,如计算器,也可以是对第三方服务的 API 调用,如查询股票价格或天气预报。在 AI Agent 的语境中,工具被设计为由 Agent 响应模型生成的函数调用而执行。
它适用于哪些用例?
AI Agent 可以利用工具来完成复杂的任务、检索信息或做出决策。工具使用设计模式常用于需要与外部系统进行动态交互的场景,例如数据库、Web 服务或代码解释器。此能力适用于多种不同的用例,包括:
- 动态信息检索: Agent 可以查询外部 API 或数据库以获取最新数据(例如,查询 SQLite 数据库进行数据分析,获取股票价格或天气信息)。
- 代码执行和解释: Agent 可以执行代码或脚本来解决数学问题、生成报告或执行模拟。
- 工作流自动化: 通过集成任务调度器、电子邮件服务或数据管道等工具,自动化重复或多步骤工作流。
- 客户支持: Agent 可以与 CRM 系统、工单平台或知识库交互以解决用户查询。
- 内容生成和编辑: Agent 可以利用语法检查器、文本摘要工具或内容安全评估器等工具来协助内容创建任务。
实现工具使用设计模式所需的元素/构建模块是什么?
这些构建模块使 AI Agent 能够执行广泛的任务。让我们看看实现工具使用设计模式所需的关键元素:
-
函数/工具模式:可用工具的详细定义,包括函数名称、用途、所需参数和预期输出。这些模式使 LLM 能够理解有哪些工具可用以及如何构建有效的请求。
-
函数执行逻辑:根据用户意图和对话上下文,管理工具何时以及如何被调用。这可能包括规划器模块、路由机制或动态确定工具使用的条件流。
-
消息处理系统:管理用户输入、LLM 响应、工具调用和工具输出之间对话流程的组件。
-
工具集成框架:将 Agent 连接到各种工具的基础设施,无论是简单的函数还是复杂的外部服务。
-
错误处理与验证:处理工具执行失败、验证参数和管理意外响应的机制。
-
状态管理:跟踪对话上下文、之前的工具交互和持久数据,以确保多轮交互的一致性。
接下来,让我们更详细地了解函数/工具调用。
函数/工具调用
函数调用是我们使大型语言模型(LLM)与工具交互的主要方式。您会经常看到“函数”和“工具”互换使用,因为“函数”(可重用代码块)是 Agent 执行任务时使用的“工具”。为了调用函数的代码,LLM 必须将用户的请求与函数的描述进行比较。为此,一个包含所有可用函数描述的模式被发送到 LLM。然后,LLM 为任务选择最合适的函数并返回其名称和参数。被选中的函数被调用,其响应被发送回 LLM,LLM 使用该信息来响应用户的请求。
为了开发者为 Agent 实现函数调用,您将需要:
- 一个支持函数调用的 LLM 模型
- 包含函数描述的模式
- 所描述的每个函数的代码
让我们以获取城市当前时间为例进行说明:
-
初始化一个支持函数调用的 LLM
并非所有模型都支持函数调用,因此检查您使用的 LLM 是否支持函数调用很重要。Azure OpenAI 支持函数调用。我们可以从初始化 Azure OpenAI 客户端开始。
# Initialize the Azure OpenAI client client = AzureOpenAI( azure_endpoint = os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT"), api_key=os.getenv("AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY"), api_version="2024-05-01-preview" ) -
创建一个函数模式:
接下来,我们将定义一个 JSON 模式,其中包含函数名称、函数作用的描述以及函数参数的名称和描述。然后,我们将把这个模式连同用户查询旧金山时间一起传递给之前创建的客户端。需要注意的是,返回的是一个工具调用,而不是问题的最终答案。如前所述,LLM 返回它为任务选择的函数名称以及将传递给它的参数。
# Function description for the model to read tools = [ { "type": "function", "function": { "name": "get_current_time", "description": "Get the current time in a given location", "parameters": { "type": "object", "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "The city name, e.g. San Francisco", }, }, "required": ["location"], }, } } ]# Initial user message messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the current time in San Francisco"}] # First API call: Ask the model to use the function response = client.chat.completions.create( model=deployment_name, messages=messages, tools=tools, tool_choice="auto", ) # Process the model's response response_message = response.choices[0].message messages.append(response_message) print("Model's response:") print(response_message)Model's response: ChatCompletionMessage(content=None, role='assistant', function_call=None, tool_calls=[ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(id='call_pOsKdUlqvdyttYB67MOj434b', function=Function(arguments='{"location":"San Francisco"}', name='get_current_time'), type='function')]) -
执行任务所需的函数代码
现在 LLM 已经选择了需要运行的函数,执行任务的代码需要被实现和执行。我们可以在 Python 中实现获取当前时间的代码。我们还需要编写代码从
response_message中提取名称和参数以获取最终结果。def get_current_time(location): """Get the current time for a given location""" print(f"get_current_time called with location: {location}") location_lower = location.lower() for key, timezone in TIMEZONE_DATA.items(): if key in location_lower: print(f"Timezone found for {key}") current_time = datetime.now(ZoneInfo(timezone)).strftime("%I:%M %p") return json.dumps({ "location": location, "current_time": current_time }) print(f"No timezone data found for {location_lower}") return json.dumps({"location": location, "current_time": "unknown"})# Handle function calls if response_message.tool_calls: for tool_call in response_message.tool_calls: if tool_call.function.name == "get_current_time": function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments) time_response = get_current_time( location=function_args.get("location") ) messages.append({ "tool_call_id": tool_call.id, "role": "tool", "name": "get_current_time", "content": time_response, }) else: print("No tool calls were made by the model.") # Second API call: Get the final response from the model final_response = client.chat.completions.create( model=deployment_name, messages=messages, ) return final_response.choices[0].message.contentget_current_time called with location: San Francisco Timezone found for san francisco The current time in San Francisco is 09:24 AM.
函数调用是大多数(如果不是全部)Agent 工具使用设计的核心,然而从头开始实现它有时可能具有挑战性。正如我们在第 2 课中所学,Agent 框架为我们提供了预构建的构建块来实现工具使用。
使用 Agent 框架的工具使用示例
以下是一些如何使用不同 Agent 框架实现工具使用设计模式的示例:
Semantic Kernel
Semantic Kernel 是一个针对 .NET、Python 和 Java 开发者使用大型语言模型(LLM)的开源 AI 框架。它通过一个称为序列化的过程自动向模型描述您的函数及其参数,从而简化了函数调用的过程。它还处理模型和您的代码之间的来回通信。使用像 Semantic Kernel 这样的 Agent 框架的另一个优点是,它允许您访问预构建的工具,例如文件搜索和代码解释器。
下图展示了 Semantic Kernel 的函数调用过程:
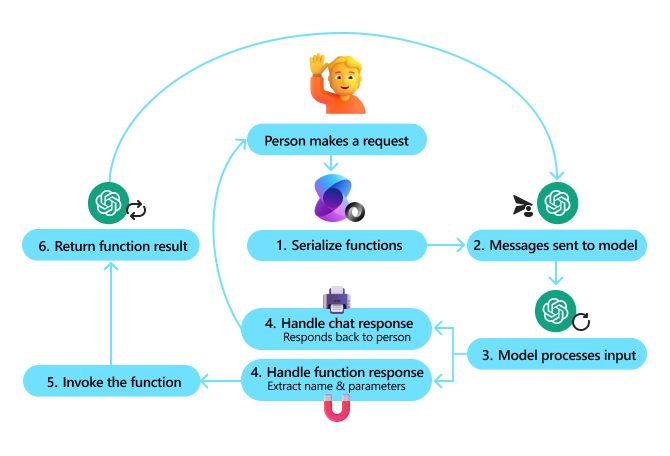
在 Semantic Kernel 中,函数/工具被称为插件。我们可以将之前看到的 get_current_time 函数通过将其转换为一个包含该函数的类来变成一个插件。我们还可以导入 kernel_function 装饰器,它接受函数的描述。然后,当您使用 GetCurrentTimePlugin 创建一个 Kernel 时,Kernel 将自动序列化该函数及其参数,在此过程中创建发送给 LLM 的模式。
from semantic_kernel.functions import kernel_function
class GetCurrentTimePlugin:
async def __init__(self, location):
self.location = location
@kernel_function(
description="Get the current time for a given location"
)
def get_current_time(location: str = ""):
...
from semantic_kernel import Kernel
# Create the kernel
kernel = Kernel()
# Create the plugin
get_current_time_plugin = GetCurrentTimePlugin(location)
# Add the plugin to the kernel
kernel.add_plugin(get_current_time_plugin)
Azure AI Agent Service
Azure AI Agent Service 是一个较新的 Agent 框架,旨在帮助开发者安全地构建、部署和扩展高质量、可扩展的 AI Agent,而无需管理底层计算和存储资源。它特别适用于企业应用,因为它是一个完全托管的服务,具有企业级安全性。
与直接使用 LLM API 进行开发相比,Azure AI Agent Service 具有一些优势,包括:
- 自动工具调用——无需解析工具调用、调用工具和处理响应;所有这些现在都在服务器端完成。
- 安全管理数据——您无需管理自己的对话状态,可以依赖线程来存储所需的所有信息。
- 开箱即用的工具——您可以用来与数据源交互的工具,例如 Bing、Azure AI Search 和 Azure Functions。
Azure AI Agent Service 中可用的工具可分为两类:
Agent 服务允许我们能够将这些工具作为一个 工具集(toolset) 来使用。它还利用 线程(threads) 来跟踪特定对话的消息历史记录。
想象您是 Contoso 公司的一名销售 Agent。您希望开发一个对话 Agent,可以回答有关销售数据的问题。
下图展示了如何使用 Azure AI Agent Service 分析销售数据:
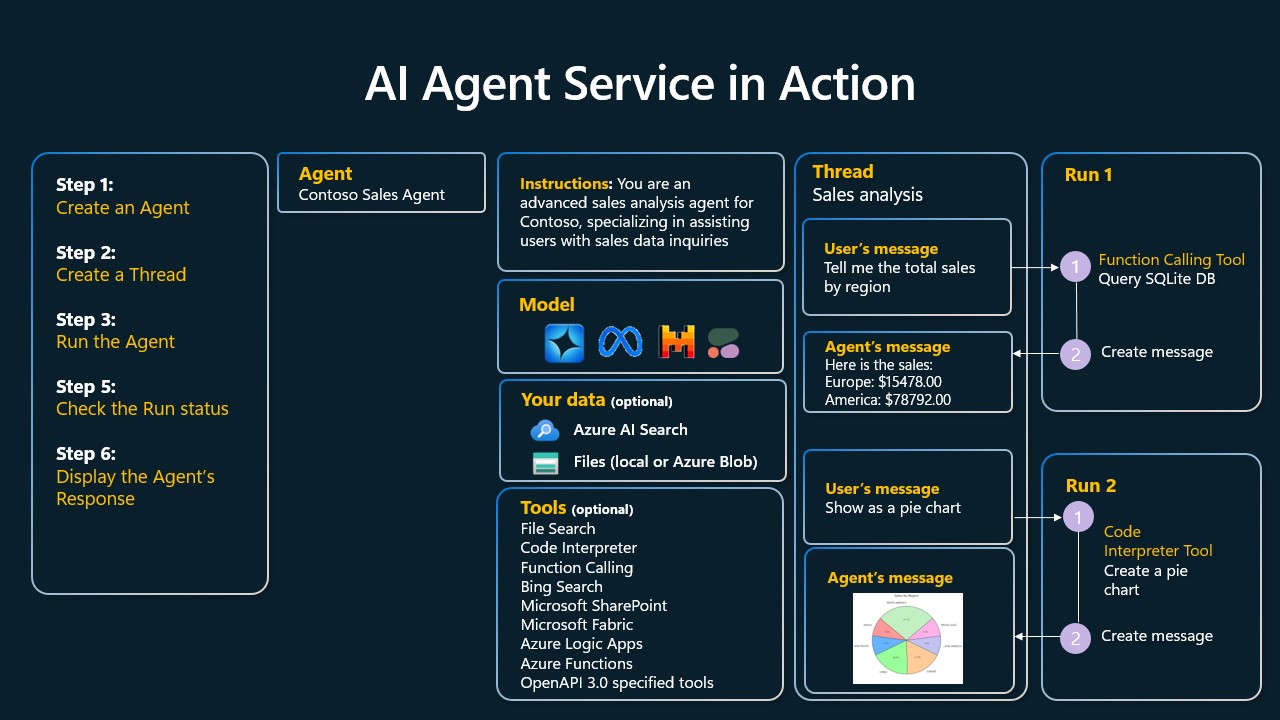
要将这些工具与服务一起使用,我们可以创建一个客户端并定义一个工具或工具集。为了实际实现这一点,我们可以使用以下 Python 代码。LLM 将能够查看工具集,并根据用户请求决定是使用用户创建的函数 fetch_sales_data_using_sqlite_query 还是预构建的代码解释器。
import os
from azure.ai.projects import AIProjectClient
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from fetch_sales_data_functions import fetch_sales_data_using_sqlite_query # fetch_sales_data_using_sqlite_query function which can be found in a fetch_sales_data_functions.py file.
from azure.ai.projects.models import ToolSet, FunctionTool, CodeInterpreterTool
project_client = AIProjectClient.from_connection_string(
credential=DefaultAzureCredential(),
conn_str=os.environ["PROJECT_CONNECTION_STRING"],
)
# Initialize function calling agent with the fetch_sales_data_using_sqlite_query function and adding it to the toolset
fetch_data_function = FunctionTool(fetch_sales_data_using_sqlite_query)
toolset = ToolSet()
toolset.add(fetch_data_function)
# Initialize Code Interpreter tool and adding it to the toolset.
code_interpreter = code_interpreter = CodeInterpreterTool()
toolset = ToolSet()
toolset.add(code_interpreter)
agent = project_client.agents.create_agent(
model="gpt-4o-mini", name="my-agent", instructions="You are helpful agent",
toolset=toolset
)
使用工具使用设计模式构建可信赖的 AI Agent 有哪些特殊考量?
LLM 动态生成的 SQL 普遍存在安全问题,特别是 SQL 注入或恶意行为(如删除或篡改数据库)的风险。虽然这些担忧是合理的,但可以通过正确配置数据库访问权限来有效缓解。对于大多数数据库,这涉及将数据库配置为只读。对于 PostgreSQL 或 Azure SQL 等数据库服务,应用程序应被分配只读(SELECT)角色。
在安全环境中运行应用程序进一步增强了保护。在企业场景中,数据通常从操作系统提取并转换到只读数据库或数据仓库中,并具有用户友好的模式。这种方法确保了数据的安全,优化了性能和可访问性,并且应用程序具有受限制的只读访问权限。
对工具使用设计模式有更多疑问?
加入 Azure AI Foundry Discord,与其他学习者交流,参加办公时间,并获得您的 AI Agent 问题解答。
额外资源
- Azure AI Agent 服务研讨会
- Contoso 创意作家多 Agent 研讨会
- Semantic Kernel 函数调用教程
- Semantic Kernel 代码解释器
- Autogen 工具
